Marek Rei의 블로그 포스트(http://www.marekrei.com/blog/paper-summaries/) 옮김
57개의 논문과 요약이라 하기에도 좀 짧은 각 3-4문장의 노트
1. A Thorough Examination of the CNN/Daily Mail Reading Comprehension Task
Danqi Chen, Jason Bolton, Christopher D. Manning. Stanford. ACL 2016.
CNN(뉴스)과 Daily Mail 데이터를 읽고 이해하는 task를 수행할 때 중요 포인트를 담았는지 체크하기 위해 Hermann et al (2015)이 제작한 데이터셋이 있다. 텍스트의 모든 entity가 비워져 있고 올바르게 채워 넣을 수 있는지 확인하는 데이터셋.
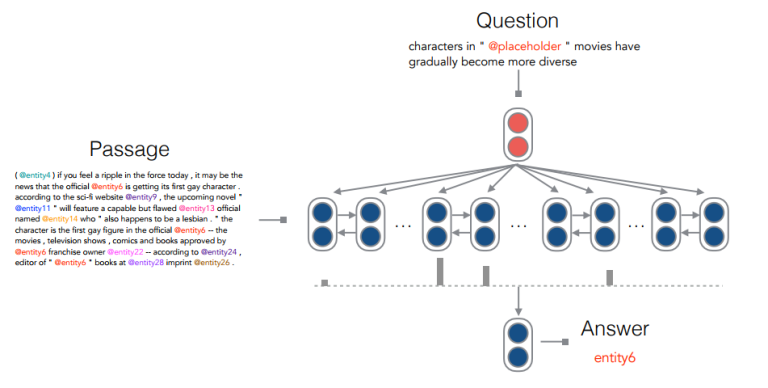
본 논문에서는 100 sample을 뽑아 인간이 직접 수행해 보았고 25% 정도의 question은 인간도 정확히 답하기 어렵다는 것을 보였다. 간단한 attention-based classifier를 이용하여 기존 performance를 상회하는 결과를 만들어 냈다.
2. Word Translation Without Parallel Data
Alexis Conneau, Guillaume Lample, Marc’Aurelio Ranzato, Ludovic Denoyer, Hervé Jégou. Facebook, Le Mans, Sorbonne. ArXiv 2017.
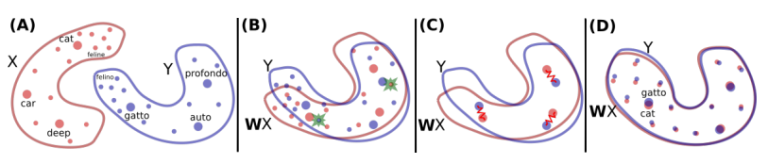
parallel corpus없이 각각 언어의 독자적은 corpus만 가지고 변역 학습을 하였다. 각 언어에 서로 다른 embedding이 학습되고, 대척되는 objective(cat<->gatto)의 mapping을 학습한다. 너무 흔하게 등장하는 단어들에는 orthogonality constraint를 준다. 또한, unsupervised stopping(기계번역에서 target word가 그만 생성되는 지점) 방법을 제시하였다.
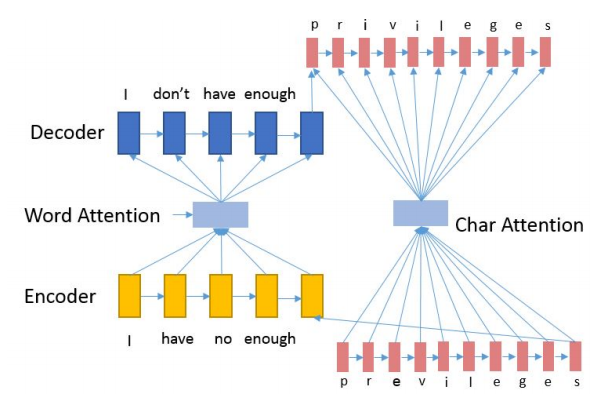
3. A Nested Attention Neural Hybrid Model for Grammatical Error Correction
Jianshu Ji, Qinlong Wang, Kristina Toutanova, Yongen Gong, Steven Truong, Jianfeng Gao. ACL 2017.
Grammatical error를 교정하는 모델, OOV words(out-of-vocabulary)가 character-based RNNs을 통과하여 decoder가 교정된 단어를 생성한다.
4. On-line Active Reward Learning for Policy Optimisation in Spoken Dialogue Systems
Pei-Hao Su, Milica Gasic, Nikola Mrksic, Lina Rojas-Barahona, Stefan Ultes, David Vandyke, Tsung-Hsien Wen, Steve Young. Cambridge. ACL 2016.
Cambridge(UK) 구역의 레스토랑 정보를 물어보면 응답해주는 spoken dialogue system을 만들었다. user의 current dialogue에 따라 해당 action과 label을 extract하여 답을 주는데, 확실한 label은 그대로 진행하고 불확실한 label에 대해서는 user에게 다시 물어본다. active learning을 통해 annotation 양을 줄여준다.
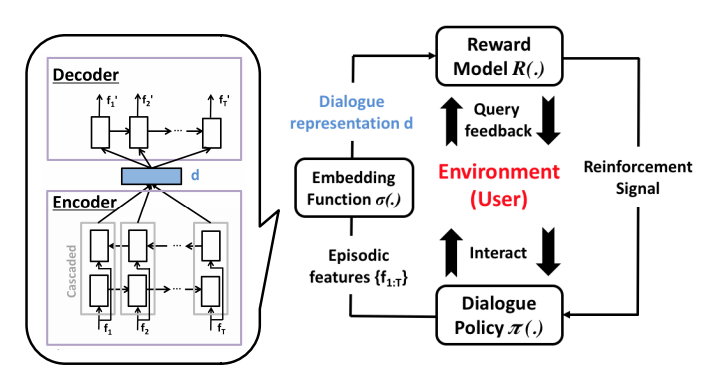
dialogue는 bi-LSTM을 통해 vector로 표현되고 dialogue success는 Gaussian Process로 모델링된다.
5. Vision and Feature Norms: Improving automatic feature norm learning through cross-modal maps
Luana Bulat, Douwe Kiela, Stephen Clark. Cambridge. NAACL 2016.
task는 feature norm을 예측하는 것이다. input word(ex. banana)를 이용하여 google에서 이미지 10장을 가져오고, 각 이미지마다 ImageNet classifier를 이용하여 feature vector를 뽑아서 각 feature마다 평균을 낸다. 이후, feature norm이 input vector(image-based, distributional, or a combination)의 결과로 train된다.

6. Adversarial examples in the physical world
Alexey Kurakin, Ian J. Goodfellow, Samy Bengio. Google, OpenAI. ArXiv.
Adversarial example이란, input data를 살짝 가공하여 classfier가 다른 class로 예측하도록 만들어진 datapoint이다. 여기서 input data에 만들어지는 변화는 아주 작아서 인간이 인식하지 못할 정도일 수도 있다.

본 논문에서는, 인위적으로 만들어 진 변화가 아닌, real world에서 카메라의 설정(화질, 밝기, contrast, noise 등)으로 얼마나 accuracy가 변화하는지 실험하였다.
7. Extracting token-level signals of syntactic processing from fMRI – with an application to POS induction
Joachim Bingel, Maria Barrett, Anders Søgaard. Copenhagen. ACL 2016.
fMRI feature를 POS tagging과 함께 이용한다. 의미적으로/문법적으로 다른 단어들을 읽을 때(text data는 해리포터) 뇌의 반응을 unsupervised POS-tagger에 word와 같이 사용하여 performance를 높였다.
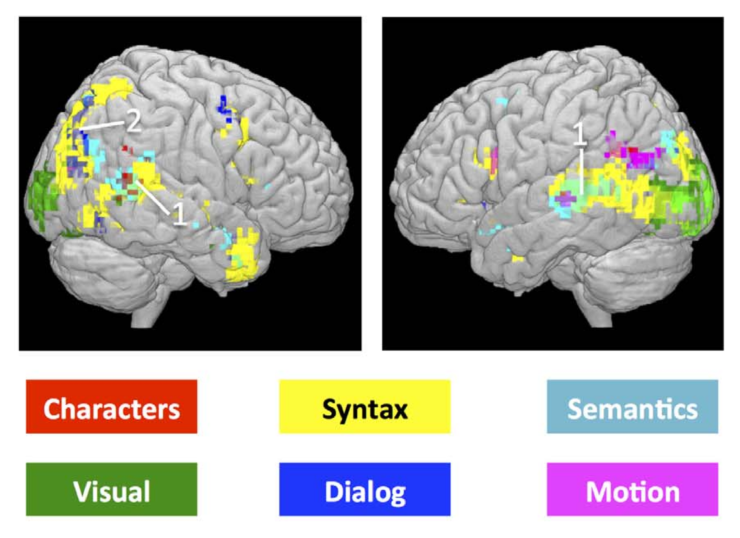
8. Joint Extraction of Events and Entities within a Document Context
Bishan Yang, Tom Mitchell. Carnegie Mellon. NAACL 2016.
kewords, entities, 그리고 events와 entities간 connection, 이렇게 3가지를 추출하는 joint model을 개발하였다. entity dection은 CRF을 이용하였고, event structure는 probabilistic graphical model을 사용한다.

9. Candidate re-ranking for SMT-based grammatical error correction
Zheng Yuan, Ted Briscoe, Mariano Felice. Cambridge. BEA Workshop 2016.
ranking SVM을 이요하여 SMT의 prediction을 re-ranking하여 생성되었던 target 문장의 grammar 오류를 정정한다.

10. Variational Neural Machine Translation
Biao Zhang, Deyi Xiong, Jinsong Su, Hong Duan, Min Zhang. Soochow University, Xiamen University. ArXiv.
Bahdanau et al. (2014)의 NMT model with alignment에, extra variational component를 추가하였다.
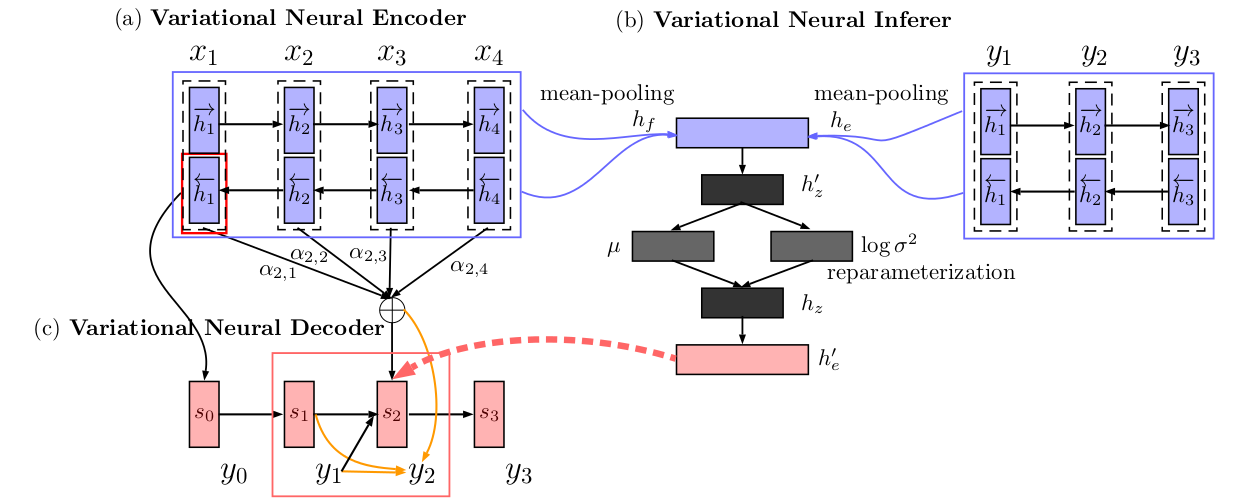
이렇게 하여 추가적으로 번역되는 문장의 의미를 가지는 latent variable z를 추적한다. 먼저 input과 output에 제한되는 z의 posterior probability를 모델링하고, input에만 제한되는 prior또한 모델링한다. 두개의 distribution은 Kullback-Leibler distance에 의해 최적화되고, testing시에는 prior만 사용된다.
11. Numerically Grounded Language Models for Semantic Error Correction
Georgios P. Spithourakis, Isabelle Augenstein, Sebastian Riedel. UCL. EMNLP 2016.
knowledge base에 제한되며 numerical value를 handling하는 LSTM language model을 만들었다.
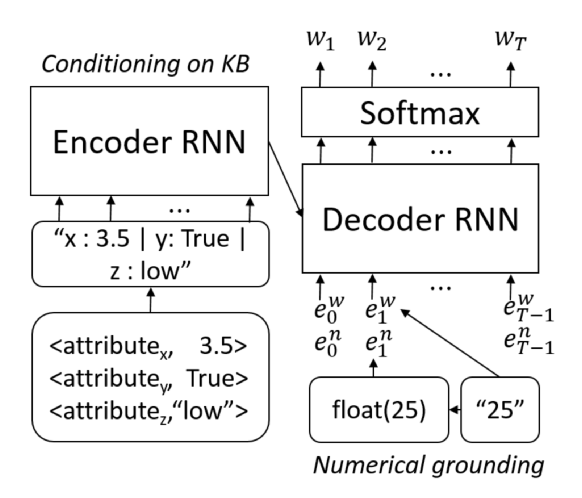
원래 우리는 “25”와 같은 token을 평범한 word embedding에 똑같이 적용하였었으나 float(25)와 같이 표현한다. 그리고 KB(knowledge base)의 모든 정보는 string으로 LSTM으로 모델링되어 main language model을 제한한다.
12. Black Holes and White Rabbits : Metaphor Identification with Visual Features
Ekaterina Shutova, Douwe Kiela, Jean Maillard. Cambridge. NAACL 2016.
“blind alley”, “honest meal” 와 같은 metaphor detection system을 개발하였다.
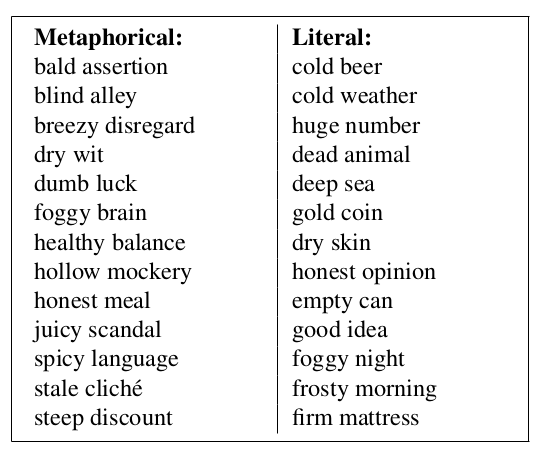
기본적으로 word embedding similarity를 이용한다. word2vec의 cosine similarity를 계산하고, phrase 별 similiarity를 계산한다.
이후, word와 phrase에 대해 vector representation을 완성하는데, words Google Image Search의 query로 사용하여 return image를 vector representation에 이용한다. 마지막으로 시스템이 linguistic vector와 visual vector를 이용하여 classify한다.
13. Counter-fitting Word Vectors to Linguistic Constraints
Nikola Mrkšić, Diarmuid Ó Séaghdha, Blaise Thomson, Milica Gašić, Lina Rojas-Barahona, Pei-Hao Su, David Vandyke, Tsung-Hsien Wen, Steve Young. Cambridge, Apple. NAACL 2016.
semantic constraints 하에 word embedding을 조절한다.
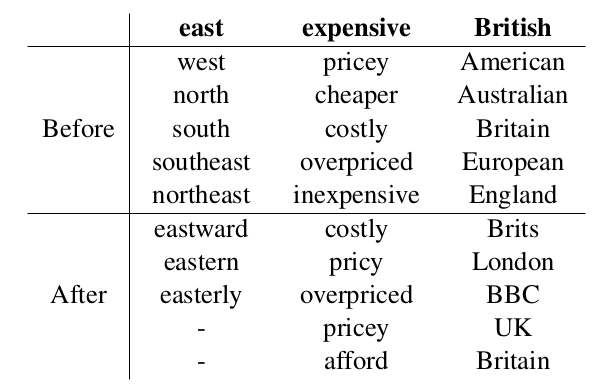
word vector들은 1) known synonyms에 high similarity를 가지고, 2) known antonyms에 low synonyms를 가지고, 3) original space에서의 similarity를 가진다.
14. Bidirectional RNN for Medical Event Detection in Electronic Health Records
Abhyuday N. Jagannatha, Hong Yu. University of Massachusetts. NAACL 2016.
780 electronic health records를 데이터셋으로 이용하여 medical events(drug events, drug dosage, etc)를 labeling한다.
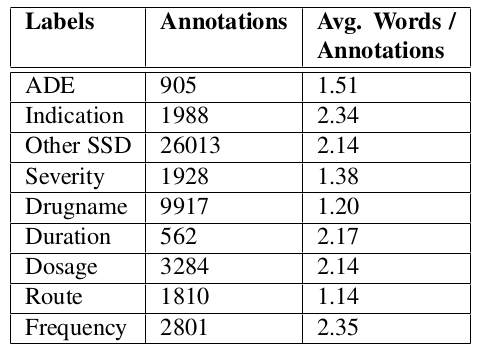
CRF, LSTM, GRU를 사용하여 실험하였고 전체 문서에 대해 학습된 GRU가 가장 좋은 performance를 냈다.
15. Symmetric Patterns and Coordinations: Fast and Enhanced Representations of Verbs and Adjectives
Roy Schwartz, Roi Reichart, Ari Rappoport. The Hebrew Universit, IIT. NAACL 2016.
word2vec skip-gram embeddings를 학습시킬 때 coordinations를 context로 이용하였다. coordination을 추출하기 위해 11개의 manual patterns를 적용시켰는데 예를 들어 “boats or planes”라 하면 “boats”는 “planes”의 context가 되고 “planes”는 “boats”의 context가 된다.
16. Comparing Data Sources and Architectures for Deep Visual Representation Learning in Semantics
Douwe Kiela, Anita L. Verő, Stephen Clark. Cambridge. EMNLP 2016.
image recognition task를 수행하던 architecture들(AlexNet, GoogLeNet, VGGNet)를 여러 데이터셋 하에 비교하였다.
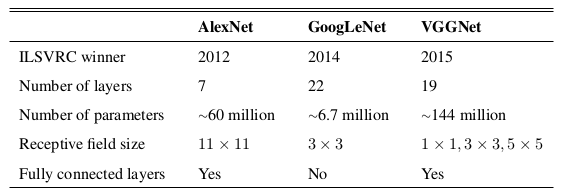
모두 비슷비슷했는데, VGGNet이 computational cost가 더 적다. ImageNet 데이터가 VGGNet에서 잘 분석되고 ESP Game dataset에서 가장 퍼포먼스가 나빴다.
17. Named Entity Recognition for Novel Types by Transfer Learning
Lizhen Qu, Gabriela Ferraro, Liyuan Zhou, Weiwei Hou, Timothy Baldwin. Melbourne. EMNLP 2016.
NER에서 source domain의 label set과 target domain의 label이 다른 문제점에 ㄷ해 다룬다.
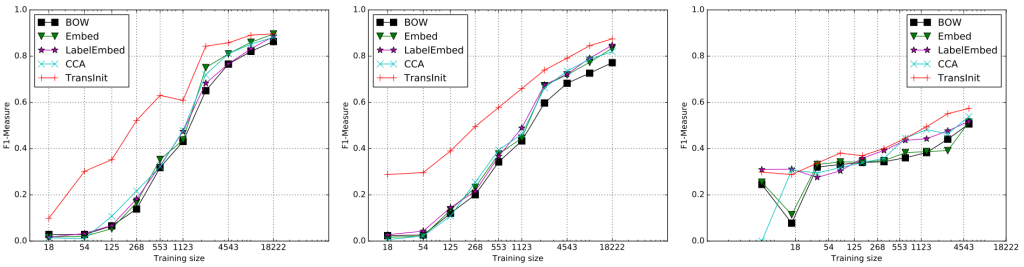
먼저 source domain에서 CRF 모델을 학습시킨 후, 모델이 예측한 label들을 LR classifier에서 weights를 생성해 또 다른 CRF model에서 target domain data에 fine-tuned하게 classify된다.
18. Hybrid computing using a neural network with dynamic external memory
Alex Graves, Greg Wayne, Malcolm Reynolds et al. DeepMind. Nature.
딥마인드에서 만든 Neural Turing Machine architecture라는데 이름만 들으면 무시무사하다…
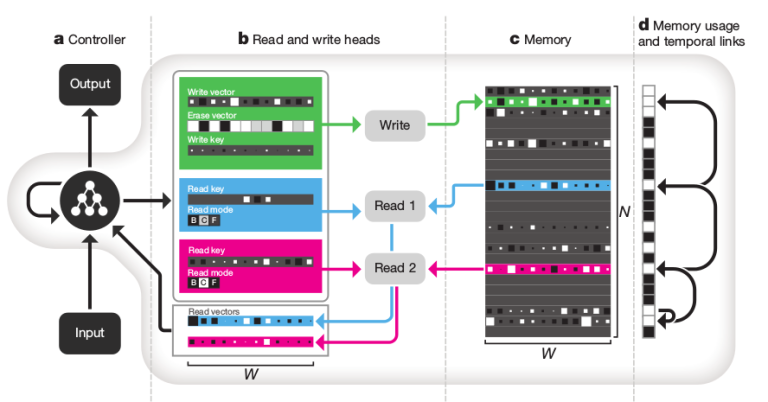
Differentiable Neural Computer (DNC) 라고 부른다. 1) attention mechanism을 이용하여 memory로 이용되는 matrix에 접속한다. 2) attention machanism을 이용하여 해당 memory에 information을 저장한다. 3) sequential information을 잘 처리하기 위해 transition matrix가 memory가 row별로 어떻게 modify되는지 추적한다.
bAbI question answering dataset, graph inference task, puzzle of arranging block의 task에서 실험해 보았다고 한다.
미쳤다 딥마인드;
19. A Neural Approach to Automated Essay Scoring
Kaveh Taghipour, Hwee Tou Ng. Singapore. EMNLP 2016.
essay 점수매기는 neural network structure
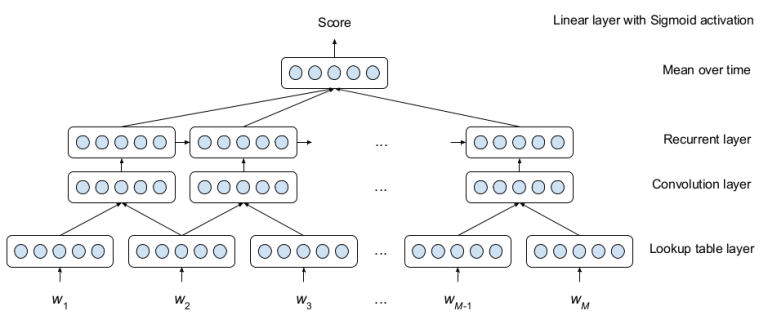
window size 3의 convolutional layer 이후 LSTM에 들어간다. LSTM output은 timestep에 따라 평균을 내고 [0,1] 범위로 scale-down하여 score가 된다. Kaggle essay scoring dataset에서 quadratic weighted Kappa로 측정되었다고 한다.
20. Globally Coherent Text Generation with Neural Checklist Models
Chloe Kiddon, Luke Zettlemoyer, Yejin Choi. Washington. EMNLP 2016.
text에 언급되어야 하는 item 리스트를 track하면서 text generation하는 모델이다.
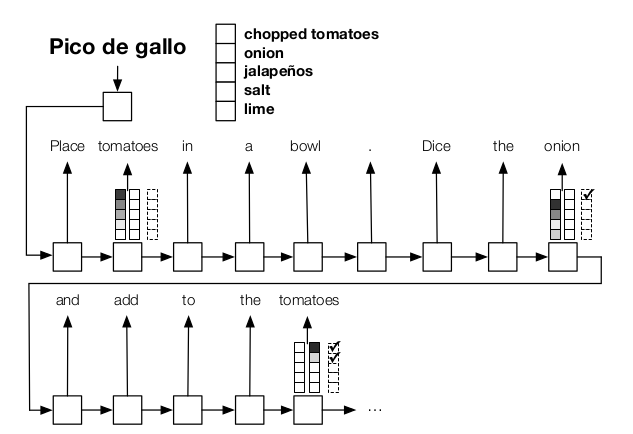
기본 시스템은 encoder-decoder GRU model을 사용하고 attention이 체크리스트의 아이템들을 따라 만들어진다.
21. Automatic Features for Essay Scoring – An Empirical Study
Fei Dong, Yue Zhang. Singapore. EMNLP 2016.
essay scoring인데 아까랑 다르게 two-level convolution을 갖는다. 첫번째는 words 레벨, 두번째는 sentence 레벨.
22. Learning Deep Structure-Preserving Image-Text Embeddings
Liwei Wang, Yin Li, Svetlana Lazebnik. University of Illinois, Georgia Tech. CVPR 2016.
image와 sentence information을 병렬로 담는 embeddings
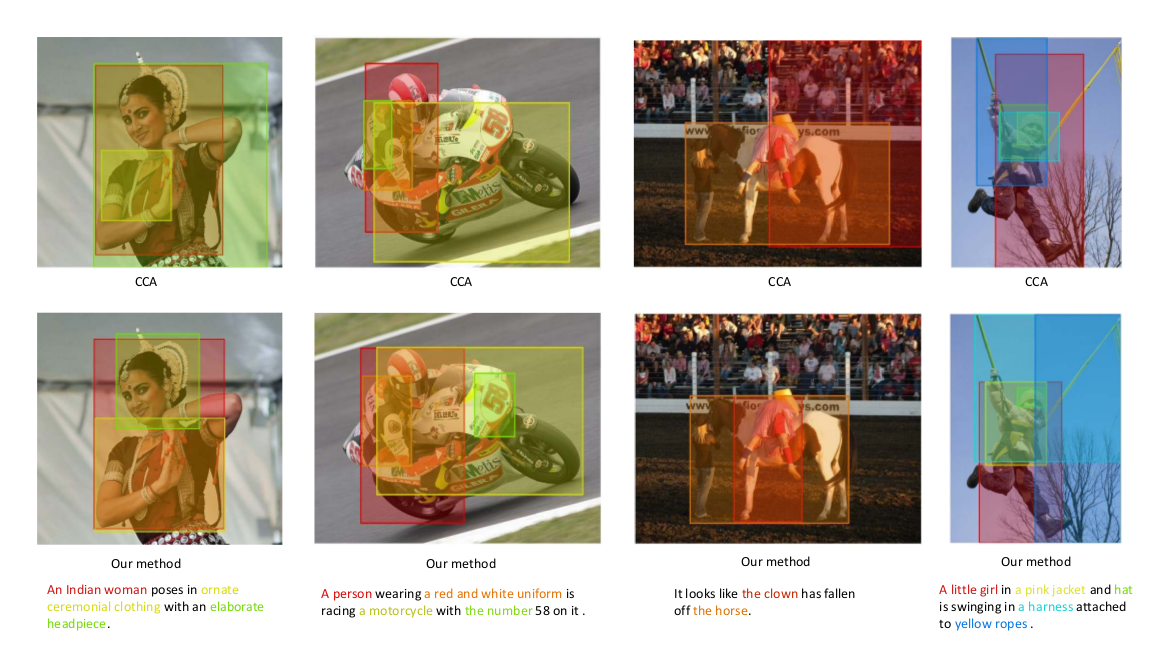
pre-trained VGG image detection network로 이미지 벡터를 뽑고, 문장 벡터는 Fisher vector를 통해 만들어진다. (word2vec, tfidf 사용됨)
23. Understanding deep learning requires rethinking generalization
Chiyuan Zhang, Samy Bengio, Moritz Hardt, Benjamin Recht, Oriol Vinyals. Google Brain, DeepMind. ICLR 2017.
저자는 잘 알려진 image recognition network의 속성들을 연구했다고 한다..
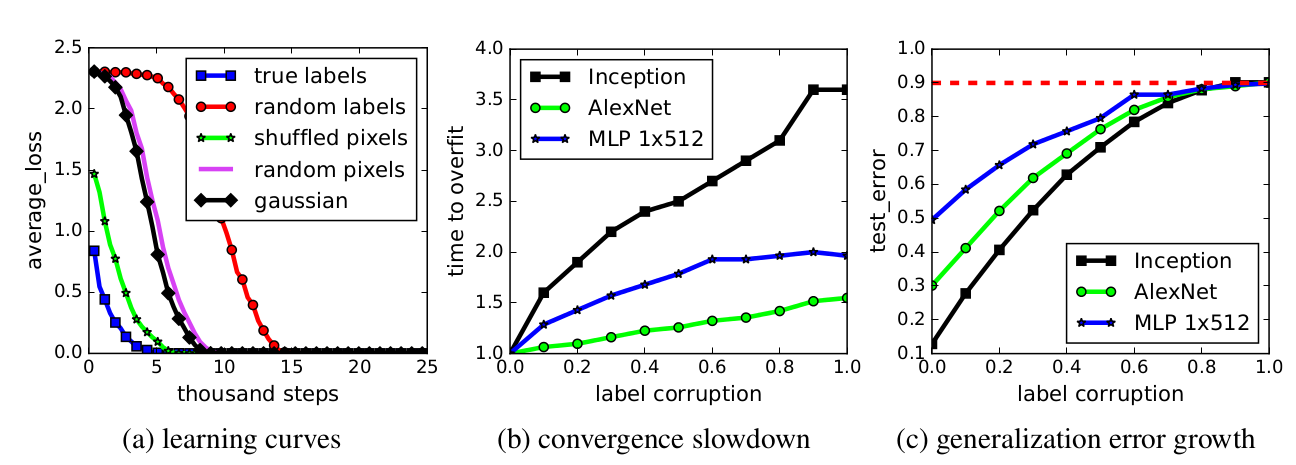
network들이 image의 label이 랜덤이어도 training set에 100% accuracy를 가질 수 있다. 혹은 image의 pixel이 랜덤이어도 그렇다. 그리고 weight decay나 dropout같은 regularization method가 overfitting을 별로 막아주고 있질 않다. 그후 그들은 massive memorization같은 method를 low-complexity pattern learning과 함께 이용하면 이런 task를 잘 처리할 수 있다고 제시한다.
갓마인드
24. Reinforcement Learning with Unsupervised Auxiliary Tasks
Max Jaderberg, Volodymyr Mnih, Wojciech Marian Czarnecki Tom Schaul, Joel Z Leibo, David Silver & Koray Kavukcuoglu. DeepMind. ICLR 2017.
main objective를 위한 보조 일(auxiliary task)도 수행하게 하는 reinforcement learning system이다.
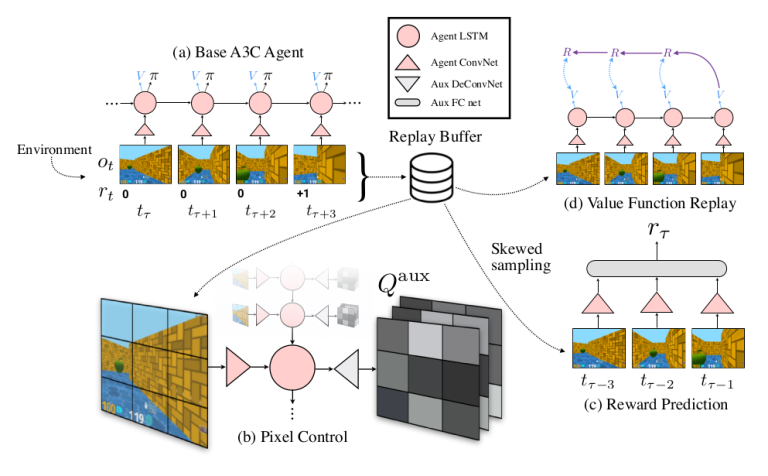
내가 강화학습을 아직 잘 모른다.
downstream reward를 예측하는 기본적인 Q-learning에 추가 system learning을 가지는데, 1) screen의 pixel을 바꾸는 별도의 policy, 2) hidden layer의 unit들을 maximally activate.. 3) biased sampling과 함게 다음 step의 reward 예측.
이 방법으로 Atari games, Labyrinth에서 learning speed와 performance를 발전시켰다.
25. Modelling metaphor with attribute-based semantics
Luana Bulat, Stephen Clark, Ekaterina Shutova. Cambridge. EACL 2017.
metaphorical word pairs를 모델링하는 attribute-based vector
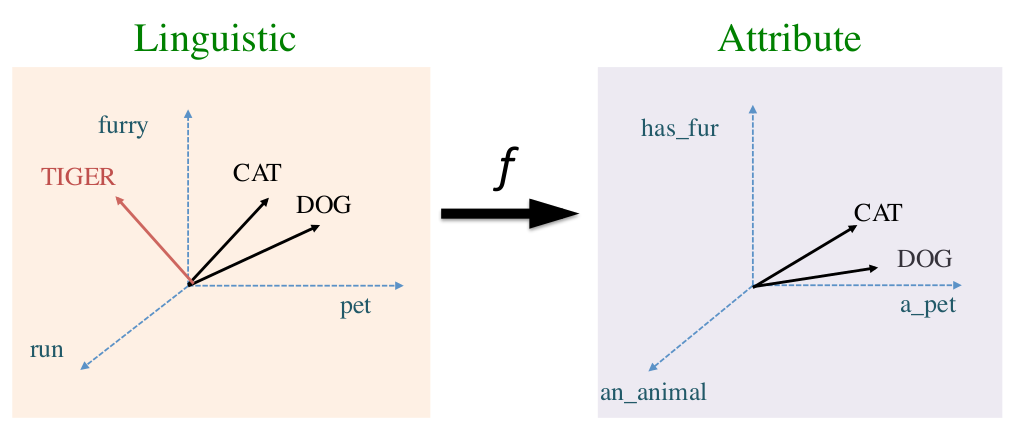
word2vec이나 count-based같은 traditional embedding이 McRae norm으로 학습된 supervised system을 이용하여 attribute vector로 매핑된다. 이 word pair들은 SVM classifier의 input으로 metaphorical word pair vs literal word pair를 detect한다.
26. Enriching Word Vectors with Subword Information
Piotr Bojanowski, Edouard Grave, Armand Joulin, Tomas Mikolov. Facebook. ArXiv 2016.
character n-gram을 이용해서 skip-gram word embedding을 확장시켰다. 각 word는 bag of character n-grams, 3-6 character long, 여기에 기존 word까지 포함된다. 각각의 embedding은 skip-gram optimization을 통해 주위 context를 예측하게 최적화된다. word similarity나 analogy task에서 performance 향상을 보였다.
27. Learning to Compose Words into Sentences with Reinforcement Learning
Dani Yogatama, Phil Blunsom, Chris Dyer, Edward Grefenstette, Wang Ling. DeepMind. ICLR 2017.
강화학습을 통해 words를 sentence로 합친다. 목적은 downstream task를 위해 좋은 parsing 방법을 찾는 것이다.
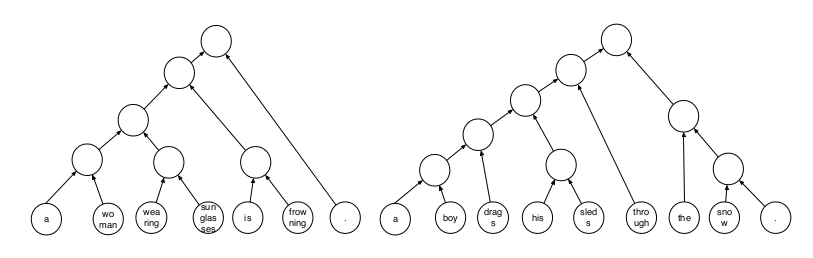
Tree-LSTM 구조를 가지는 neural shift-reduce parser를 이용한다. downstream task의 objective function하에 시스템이 통째로 reinforcement learning으로 학습된다.
28. Identifying beneficial task relations for multi-task learning in deep neural networks
Joachim Bingel, Anders Søgaard. Copenhagen. EACL 2017.
multi-task learning에서 서로 다른 task의 combination의 benefit을 찾는다.
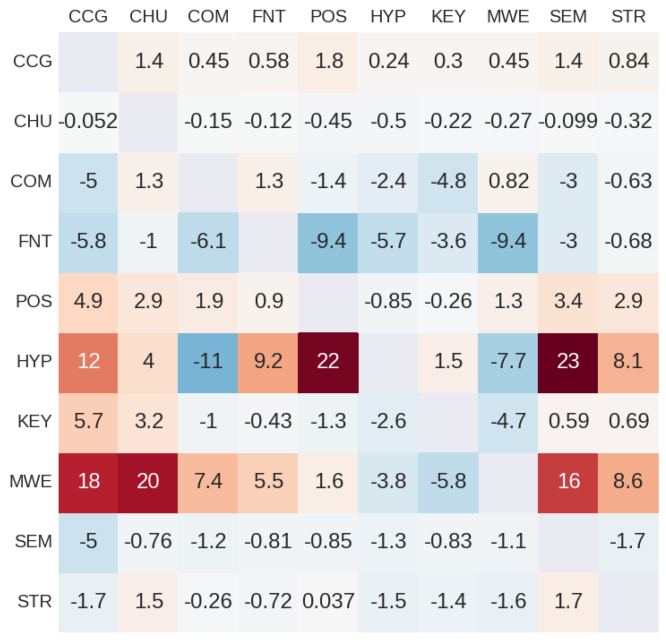
10개의 sequence labeling dataset에서 가능한 모든 pair에서 실험했다. multi-task learning이 main task가 빨리 안정기로 들어가며 auxiliary task는 그러지 않을 때 도움이 됨을 보인다. 모든 main task에게 beneficial한 auxiliary task는 없었지만 chunking과 semantic tagging이 그나마 제일 performance가 좋았다.
29. Literal and Metaphorical Senses in Compositional Distributional Semantic Models
E. Darío Gutiérrez, Ekaterina Shutova, Tyler Marghetis, Benjamin K. Bergen. UCSD, Cambridge, Bloomington. ACL 2016.
mataphor를 위해 specialized된 compositional semantic model.
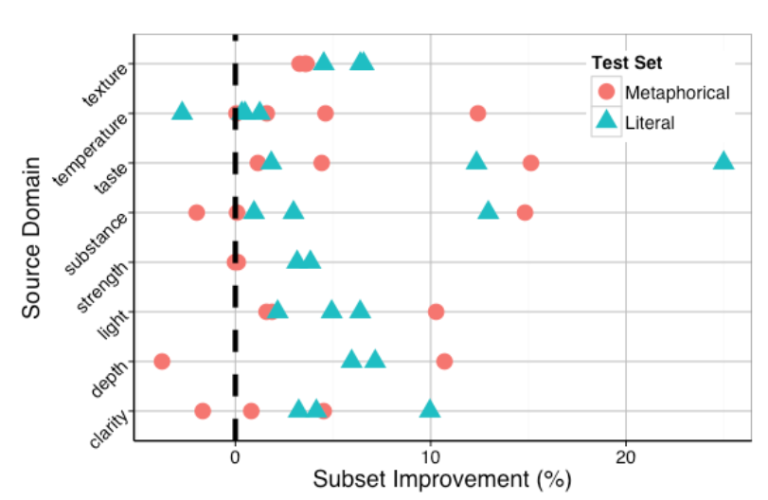
먼저 그들은 23가지의 adjective를 가지는 8592 쌍의 adjective-noun phrases dataset을 만들었고, metaphorical인지 literal인지 annotate하였다. 그리고 compositional model이 adjective-specific weight matrix를 이용하여 noun을 base로 phrase vector를 예측하게 하였다. 그리고 이 구조가 metaphor identification task에 더 좋음을 보였다.
30. Data Noising as Smoothing in Neural Network Language Models
Ziang Xie, Sida I. Wang, Jiwei Li, Daniel Levy, Aiming Nie, Daniel Jurafsky, Andrew Y. Ng. Stanford. ICLR 2017.
RNN language model에서의 효과적인 noising technique 연구
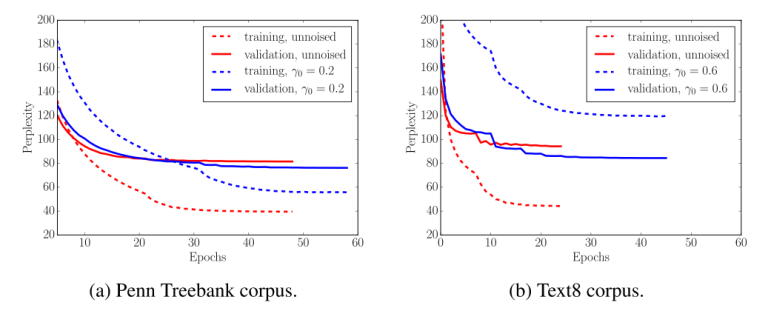
dropout이랑 비슷한 방식으로 랜덤하게 words를 blank token으로 교체하는 기존 noising technique이 있었다. 여기서는 n-gram smoothing에서 영감을 얻어 replace될 words를 랜덤이 아니라 잘 고르는 방식을 소개하고 language modeling이나 NMT task에서 performance 향상을 보였다.
31. Neural Belief Tracker: Data-Driven Dialogue State Tracking
Nikola Mrkšić, Diarmuid Ó Séaghdha, Tsung-Hsien Wen, Blaise Thomson, Steve Young. Cambridge, Apple. ACL 2017.
dialogue state tracking을 위한 neural model이다. user와 system에서의 최신 context 기반으로 가능한 slot-value pair마다 binary decision을 만든다. context와 slot-value option을 word representation을 합치거나 convnet을 이용하여 만들어진 vector로 binary output을 예측한다. 두 개의 dialogue dataset에서 improvement를 보였다.
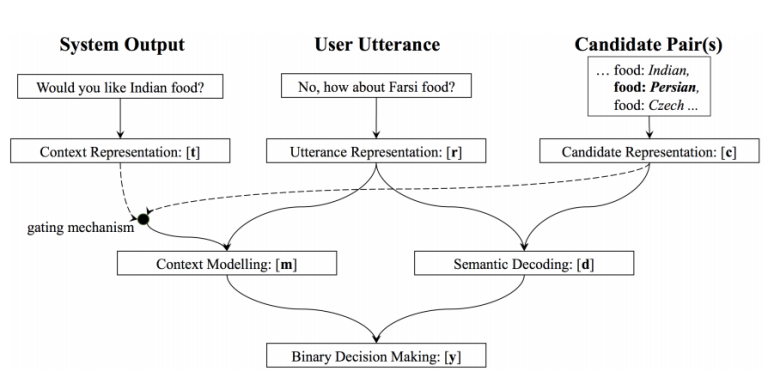
32. Neural Architectures for Fine-grained Entity Type Classification
Sonse Shimaoka, Pontus Stenetorp, Kentaro Inui, Sebastian Riedel. Tohoku, UCL. EACL 2017.
Bi-LSTM, attention, hand-engineered features, label hierarchy를 이용하여 entity type classification하는 모델. Figer, OntoNotes dataset에서 성능 향상을 보였다.
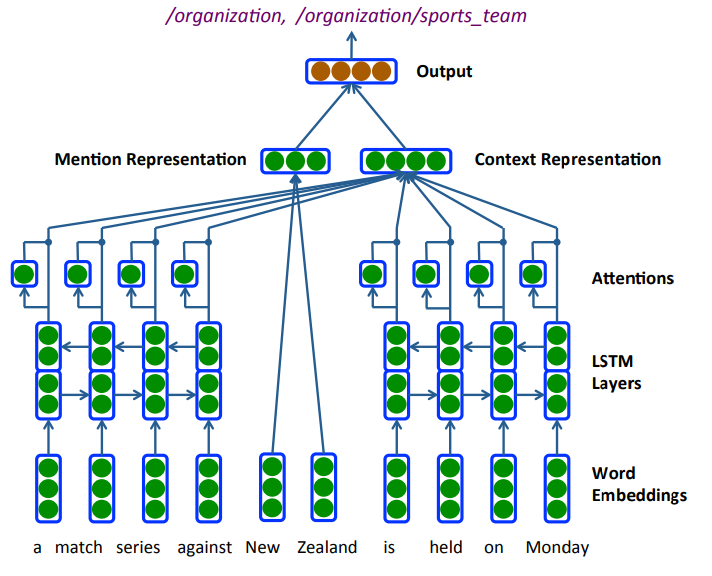
33. Recurrent Additive Networks
Kenton Lee, Omer Levy, Luke Zettlemoyer. Washington, Allen Institute. ArXiv 2017.
LSTM을 단순화 시킨 Recurrent Additive Network(RAN)를 만들었다. 몇 몇 non-linearities와 weighted components를 제거하였다.
34. A Sensitivity Analysis of (and Practitioners’ Guide to) Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification
Ye Zhang, Byron Wallace. UT Austin. IJCNLP 2017.
9가지 문장 분류 데이터셋에서 single-layer CNN의 최적의 hyperparameter를 분석하였다.
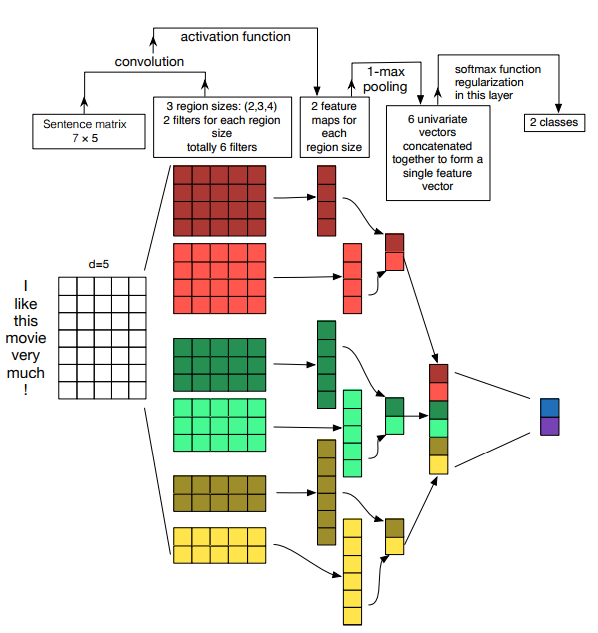
filter size와 feature map 갯수는 dataset에 따라 다르며 다 시도하여 찾아야 하고, activation function으로는 ReLU와 tanh가 가장 좋다. 1-max pooling이 좋고, feature map이 많아 질수록 dropout이 좋다.
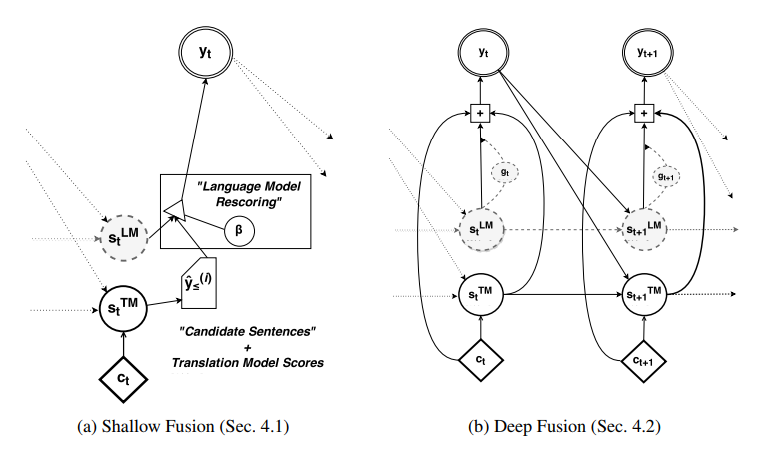
35. On Using Monolingual Corpora in Neural Machine Translation
Caglar Gulcehre, Orhan Firat, Kelvin Xu, Kyunghyun Cho, Loic Barrault, Huei-Chi Lin, Fethi Bougares, Holger Schwenk, Yoshua Bengio. Montreal, METech, Maine. Computer Speech and Language 2016.
기계번역에 쓰이는 seq2seq model과 language model을 합쳤다. pre-train된 seq2seq model과 neural language model에서의 hidden states를 합쳐서 예측을 진행한다.
36. Semi-supervised sequence tagging with bidirectional language models
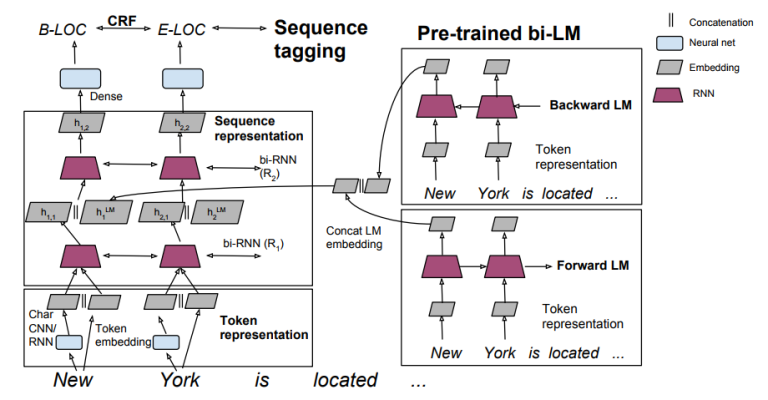
Matthew E. Peters, Waleed Ammar, Chandra Bhagavatula, Russell Power. Allen Institute. ACL 2017.
sequence labeling model에 pre-trained language model을 이용한다. baseline 모델은 two-layer LSTM/GRU이고, 본 논문에서는 pre-trained language model의 hidden state를 첫번째 LSTM layer의 아웃풋과 합친다. NER과 chunking task에서 성능 향상을 만들었다.
37. Weakly Supervised Part-of-speech Tagging Using Eye-tracking Data
Maria Barrett, Joachim Bingel, Frank Keller, Anders Søgaard. Copenhagen. ACL 2016.
POS-tagging task에 eye tracking을 효과적으로 사용하였다…….
가정은 읽는 사람이 closed class words에는 빠르게 눈이 지나가고 ambiguous words에는 눈이 좀 더 오래 멈춰 있다는 것.
second-order HMM에 eye tracking feature를 사용하였고 성능 향상을 보였다. 놀랍게도, eye tracking feature를 training token의 type별로 평균내서 사용하는 것이 더 잘 나왔는데, 이는 eye tracking feature는 학습 시에만 사용하여도 된다는 것을 보여준다.
38. Massive Exploration of Neural Machine Translation Architectures
Denny Britz, Anna Goldie, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc Le. Google Brain. EMNLP 2017.
encoder-decoder NMT model 여러가지를 비교 분석하였다. LSTM이 GRU보다 좋고 2 bidirectional layer면 충분하다. additive attention, well-tuned beam search이 성능이 제일 좋다.
39. Learning to Reason: End-to-End Module Networks for Visual Question Answering
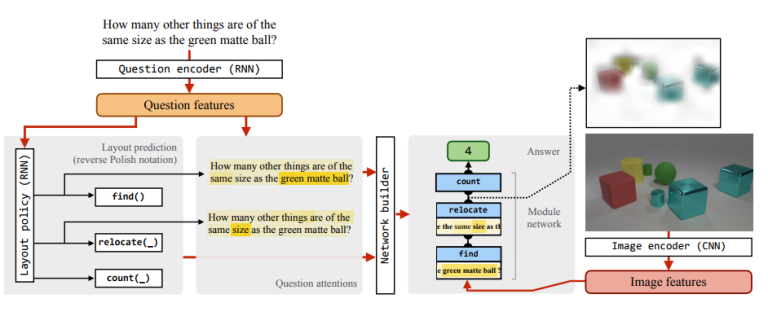
Ronghang Hu, Jacob Andreas, Marcus Rohrbach, Trevor Darrell, Kate Saenko. Berkeley, Facebook, Boston. ICCV 2017.
visual question answering을 위한 modular neural architecture를 만들었다. seq2seq component가 textual question으로 find()나 compare()같은 neural module의 seqeunce를 예측하고, end-to-end로 neural module sequence가 학습된다.
40. Automatic Annotation and Evaluation of Error Types for Grammatical Error Correction
Christopher Bryant, Mariano Felice, Ted Briscoe. Cambridge. ACL 2017.
grammar error의 타입을 자동으로 제공하는 툴킷이다. 기존 문장과 고쳐진 문장을 input으로 정렬하여 error의 위치를 추정하고 rule기반으로 error type을 부여한다.
41. Dynamic Evaluation of Neural Sequence Models
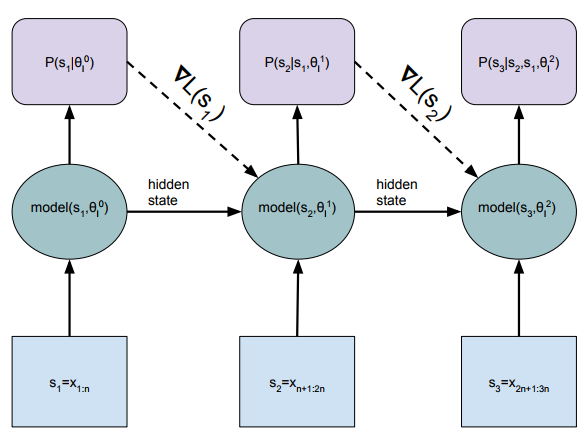
Ben Krause, Emmanuel Kahembwe, Iain Murray, Steve Renals. Edinburgh. ArXiv 2017.
observed sequence 기반으로 update parameters. 보통 LSTM language model이 sequence를 전부 돌리고 parameter update하고 hidden state가 초기화되는데, dynamic evaluation은 초기화 안하고 끝까지 쭉 도는 와중에 계속 gradient descent 해 준다.
42. Unsupervised Machine Translation Using Monolingual Corpora Only
Guillaume Lample, Ludovic Denoyer, Marc’Aurelio Ranzato. Facebook, Sorbonne. ArXiv 2017.
parallel corpora 없이, seq2seq, autoencoder, adverarial objective를 통해 NMT 구축.
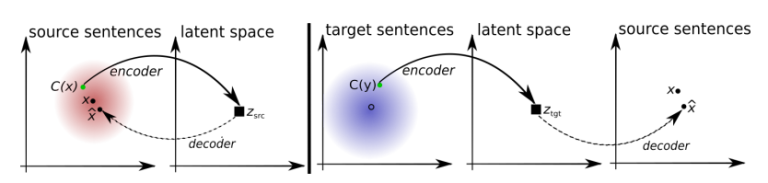
43. Assessing the Ability of LSTMs to Learn Syntax-Sensitive Dependencies
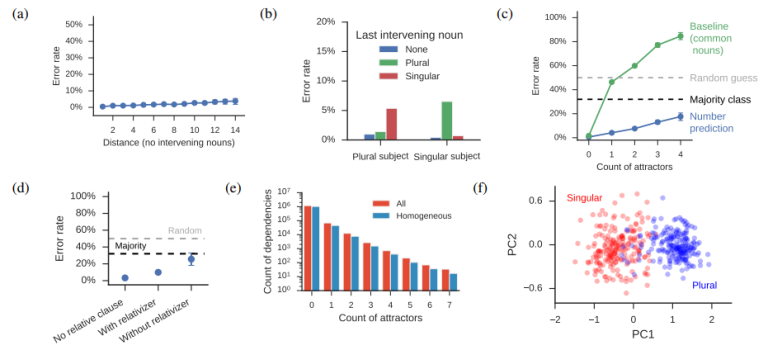
Tal Linzen, Emmanuel Dupoux, Yoav Goldberg. ENS, Bar Ilan. TACL 2017.
LSTM이 long-distance dependency를 얼마나 잘 capture하는가에 대한 연구. subject noun이 distractors에 의해 분리되어 있을 때, verb agreement(singular or plural)을 예측하는 task에서 LSTM이 잘 해결함.
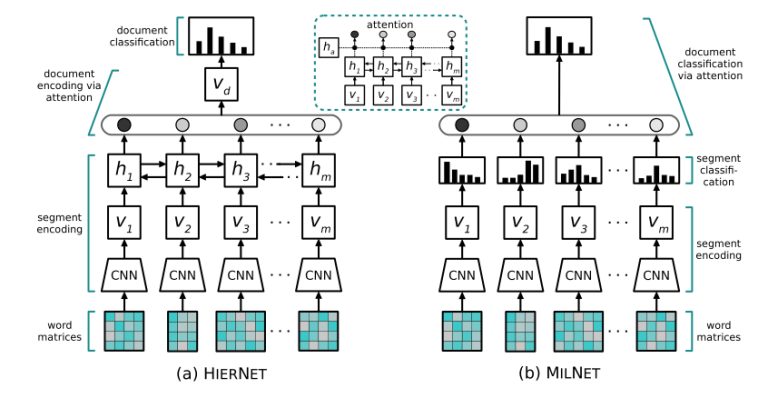
44. Multiple Instance Learning Networks for Fine-Grained Sentiment Analysis
Stefanos Angelidis, Mirella Lapata. Edinburgh. ArXiv 2017.
document sentiment classification을 위한 모델, 동시에 sentence-level sentiment prediction들도 얻어낸다. convnet으로 sentence-level representation들을 만든 다음, 얘네들을 이용해서 sentence-level sentiment label probability distribution을 만들고, fixed weight vector나 attention mechanism을 이용해 다 합친다. 그리고 200 document가 sentence별로 annotate된 데이터셋도 만들어 주셨다.
45. Learning how to Active Learn: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Meng Fang, Yuan Li, Trevor Cohn. Melbourne. EMNLP 2017.
Active Learning(어떤 데이터를 annotate해서 traning set에 추가할 지 결정하며 진행되는 학습)을 reinforcement learning으로 해결하였다. Q-learning network가 각 sentence가 annotate 되야 할 지 아닐 지 결정한다. 여기서 이 network는 main task의 performance improvement를 기준으로 학습되었다. evaluation은 NER task에서 진행하였다.
46. On the State of the Art of Evaluation in Neural Language Models
Gábor Melis, Chris Dyer, Phil Blunsom. Deepmind, Oxford. ArXiv 2017.
language modeling을 위한 recurrent architecture 3가지를 비교하였다, LSTM, Recurrent Highway Network, NAS architecture. basic LSTM이 최고였단다.
47. Dynamic Routing Between Capsules
Sara Sabour, Nicholas Frosst, Geoffrey E Hinton. Google Brain. NIPS 2017.
구분된 다른 convolutional layer들의 information을 동시에 가져와 attention mechanism에 사용하는 모델. custom squashing function이 필요했다.
48. Multilingual Part-of-Speech Tagging with Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Models and Auxiliary Loss
Barbara Plank, Anders Søgaard, Yoav Goldberg. Groningen, Copenhagen, Bar-Ilan. ACL 2016.
char-LSTM, word-LSTM을 이용한 POS-tagging에서 word에 POS와 함께 등장확률을 같이 예측하게 하고, 이것까지 loss에서 어찌저찌 계산하게 했다. low-frequency word에 tagging accuracy가 올라갔다.
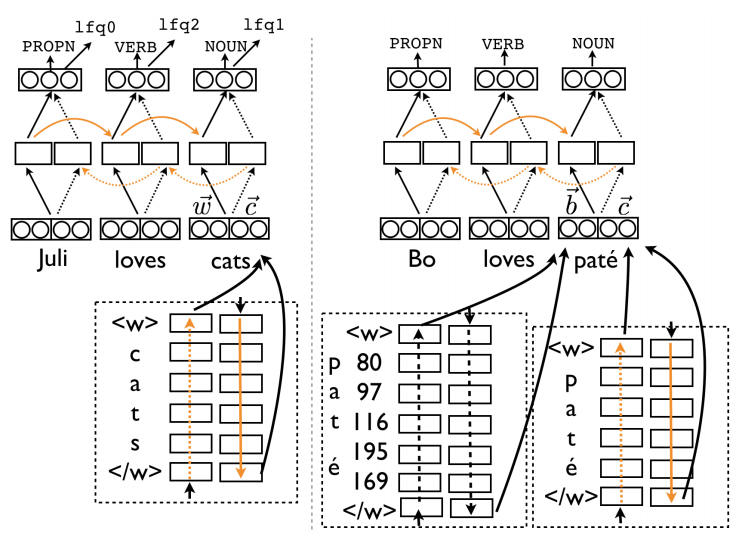
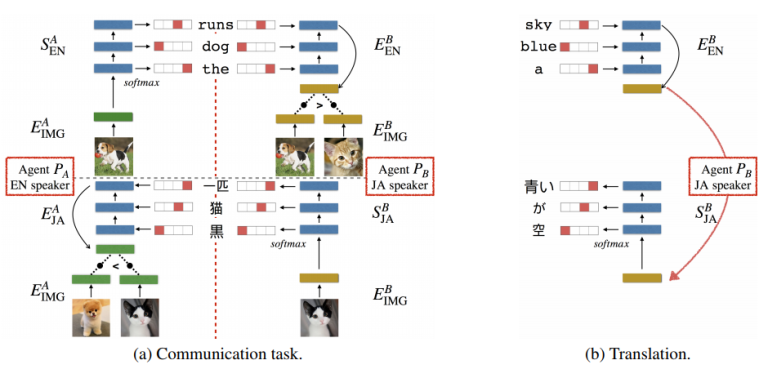
49. Emergent Translation in Multi-Agent Communication
Jason Lee, Kyunghyun Cho, Jason Weston, Douwe Kiela. Facebook. ArXiv 2017.
이미지를 input으로 각 언어로 예측된 캡션을 연결하는 방식으로 학습된다. Gumbel-softmax를 사용한다.
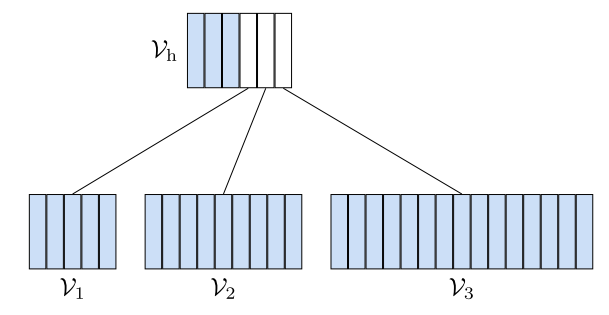
50. Efficient softmax approximation for GPUs
Edouard Grave, Armand Joulin, Moustapha Cissé, David Grangier, Hervé Jégou. Facebook. ICML 2017.
adaptive softmax라고, softmax를 2-level hierarchy를 갖게 만들었다. 아주 큰 vocabulary들을 가질 때 장점이 있다. 특히 GPU에서의 matrix-matrix vector operation을 이용해 computational time을 줄인다.
여기부터 저 포스트 쓴 사람 본인 논문들(Marek Rei)
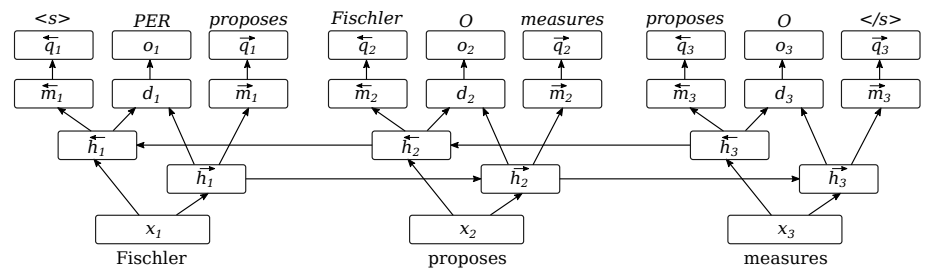
51. Semi-supervised Multitask Learning for Sequence Labeling
Marek Rei. Cambridge. ACL 2017.
sequence labeling을 위한 bi-LSTM 모델을 기본으로, tagger가 학습될 때 forward-LSTM은 다음 word를, backward-LSTM은 이전 word를 예측하게 한다.
52. Grasping the Finer Point: A Supervised Similarity Network for Metaphor Detection
Marek Rei, Luana Bulat, Douwe Kiela, Ekaterina Shutova. Cambridge, Facebook. EMNLP 2017.
metaphorical phrase detection을 위한 구조, gating mechanism을 이용하여 각 단어를 다른 단어에 의존하게 만들고 weighted cosine similarity의 neural version을 이용하여 예측을 하고 hinge loss를 이용하여 model을 최적화한다.
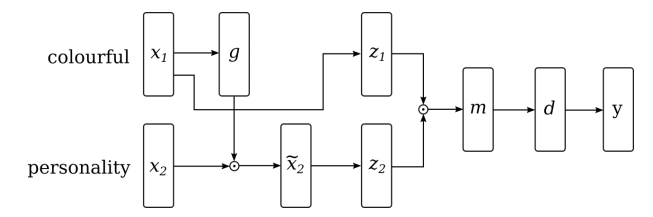
53. Neural Sequence-Labelling Models for Grammatical Error Correction
Helen Yannakoudakis, Marek Rei, Øistein E. Andersen, Zheng Yuan. Cambridge. EMNLP 2017.
neural sequence labeling model을 이용하여 token별 correctness probability를 계산한 후 대상 가능한 correction candidate들을 rerank한다. error correction을 위해 error detection을 발전시키는 방식.
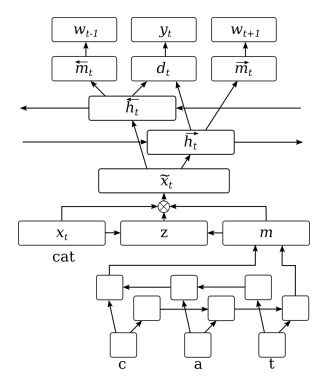
54. Artificial Error Generation with Machine Translation and Syntactic Patterns
Marek Rei, Mariano Felice, Zheng Yuan, Ted Briscoe. Cambridge. BEA 2017.
grammatical error detection을 위해 인위적으로 train data를 늘린다. 여기서 새로 만든 데이터가 incorrect English여야 함. 1) regular machine translation 모델로 correct English로 incorrect English를 만든다. 혹은, 2) POS tag를 이용해서 인위적인 error를 집어 넣는다.

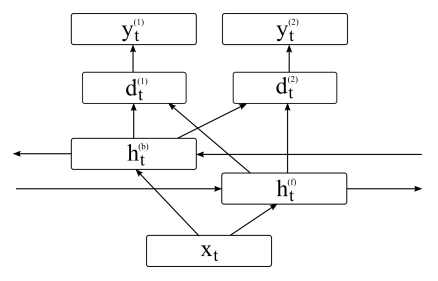
55. Auxiliary Objectives for Neural Error Detection Models
Marek Rei, Helen Yannakoudakis. Cambridge. BEA 2017.
error detection에 neural sequence labeling approach를 사용하는데, joint learning approach trained with parallel labels on in-domain data를 이용하여 성능 향상을 만들었다.
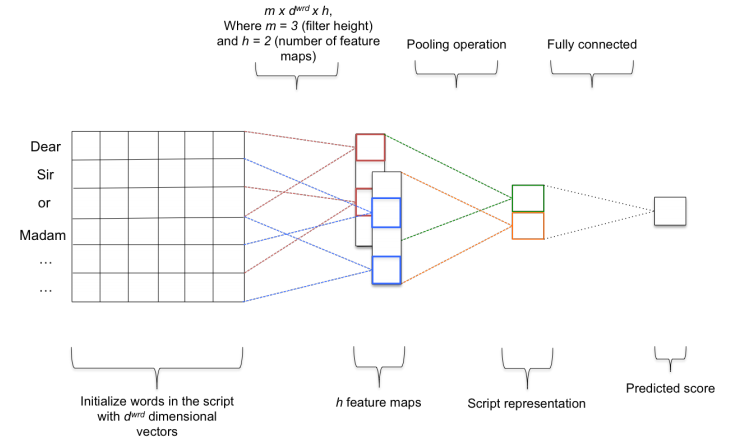
56. An Error-Oriented Approach to Word Embedding Pre-Training
Youmna Farag, Marek Rei, Ted Briscoe. Cambridge. BEA 2017.
word embedding이 grammatical sentenece와 ungrammatical sentence를 구분하는 objective를 가지고 pre-trained되고 요걸 essay scoring에 사용한다.
57. Detecting Off-topic Responses to Visual Prompts
Marek Rei. Cambridge. BEA 2017.
뜬금 없는 response를 detecting하는 모델, visual prompt를 포함한다. LSTM을 통해 composing된 text와 image representation을 이용하여 confidence score를 계산한다.

끝!
괜히 했다!! 힘들었다!!!